In Word, a bullet is a symbol (e.g. an asterisk, a dot, a small square, etc) placed before text, especially in a list, to emphasize it. Bullets or Numbering (using numerals, letters) are used to sort a list of items , or to emphasize certain points or lists in a document. It is often more appropriate to use Numbering for a list, where the order in which each item of the list appears is important. Bullets, on the other hand, are better suited for lists in which the order or sequence in which each item of the list appears is not important. In other words, use bullets to sort a list in which items in the list can appear in any random position; while you should use numbering to sort a list in which each item of the list must appear in a logical order. For example, if you are analyzing your activities for a day, it will be logical to start from the things you did in the morning, followed by afternoon, and then evening activities. Note, however, that there's no special rule of the thumb to this. Adding bullets or numbers to a list makes it easier to read the list, as well as sort them. You can create a multilevel lists, in which an outline of a document is arranged in a hierarchical order on the list.
Bullets and numbering can be created quickly using the Automatic Formatting feature, Formatting toolbar, or using the Bullets and Numbering dialog box.
Creating a Bulleted List Using the Automatic Formatting Feature
Using the Automatic Formatting feature, you get bullets and numbers automatically while you type. Follow these steps to create a bulleted list using the Automatic Formatting feature in Word.Before entering the first character in the list,
- Type an asterisk (*) and then press the SPACEBAR or the TAB key.
- Type the first item of the list you want to create and then press ENTER. Word automatically changes the asterisk into a bullet and sets the appropriate spacing.
- Repeat step 2 above for each item. To end the list, press ENTER twice.
 |
| Fig: Adding bullets using Automatic Formatting |
Creating a Bulleted or Numbered List Using the Formatting Toolbar
- Type the first item of the list you want to create.
- On the Formatting toolbar, click Numbering to add numbers, or click Bullets to add bullets.
- Press ENTER.
- Type the next item of the list and then press ENTER again.
- Repeat step 4 above for each new item in the list.
- Press ENTER twice to stop adding bullets or numbers.
Alternatively,
- Type the first item of the list to be created.
- Press ENTER.
- Type the next item and press ENTER again.
- Repeat step 3 above for each new item.
- After you typed the last item, press ENTER twice to stop adding bullets or numbering.
- Select the paragraphs you have created.
- On the Formatting toolbar, click Numbering to add numbers, or click Bullets to add bullets to the paragraphs to create a list.
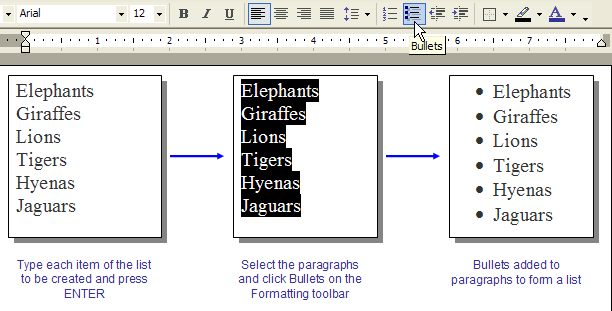 |
| Fig: Adding bullets using the Formatting toolbar |
Converting Bullets to Numbers, and Vice Versa
- Select the list.
- Do one of the following.
- To convert from bullets to numbers, click Numbering on the Formatting toolbar.
- To convert from numbers to bullets, click Bullets on the Formatting toolbar.
Creating a Bulleted or Numbered List Using the Bullets and Numbering Dialog Box
 |
| Fig: Bullets and Numbering dialog box |
The Bullets and Numbering dialog box enables you to choose from a wider range of bullets or numbering options. Here are the steps:
- If you have already created the paragraphs, select them and then perform the following steps. If you have not already typed paragraphs, just perform the following steps. All you'll need to do afterward is press ENTER and type the next item.
- On the Format menu, click Bullets and Numbers. The Bullets and Numbers dialog box is displayed.
- To create a Bulleted list
- Click the Bulleted tab in the Bullets and Numbering dialog box.
- Click the bullet list style you want.
- To create a Numbered list
- Click the Numbered tab on the Bullets and Numbering dialog box.
- Click the numbered list style you want.
- Click OK.
Format Bullets or Numbers Differently than the Text in a List Using the Formatting Toolbar
When you select a list and change its character formats (like color, size, style), the changes apply to both the bullets or numbers and the text. However, using the Formatting toolbar, you can quickly change bulleted or numbered format in a list without making changes to the text in the list. For example, you can format numbers or bullets with a different font color or font style than the text in the list.
- Click a bullet or number in a list. All the bullets or numbers in the list are highlighted.
- On the Formatting toolbar, click the options (such as Font Size, Font Color, Italic, etc) you want.
 |
Removing Bullets and Numbers
Bullets and numbers can be easily removed from a list. You can do this using either the formatting toolbar or using the Bullets and Numbers dialog box.To remove bullets or numbering using the Formatting toolbar
- Select the list you want to remove bullets and numbering from.
- Do one of the following
- To remove numbering from a list, on the Formatting toolbar,click Numbering.
- To remove bullets from a list on the Formatting toolbar, click Bullets.
To remove bullets or numbering using the Bullets and Numbering dialog box
- Select the list from which you want to remove bullets or numbering.
- On the Format menu, click Bullets and Numbers.
- Click one of these tabs: Bulleted, Numbered, or Outline Numbered.
- Click None.
- Click OK.
Creating an Outline (Multilevel) Numbered List
In Word, you can create a list by applying bullets or numbering to paragraphs and then arranging them in a hierarchical structure. The resulting list will form an Outline Numbered List. An outline numbered list is a list created to apply a hierarchical structure to any list or document. In this case, a document can have up to nine levels, but Word does not apply built-in heading styles to the items in the list. An outline numbered list has more than one level in which various styles of bullets or numbers or both are used together, but on different levels. You can also create a custom outlined bullet or numbering scheme using the Customize button.
 |
| Fig: Bullets and Numbering dialog box showing Outline Numbered list styles |
To create an outlined list
- On the Format menu, click Bullets and Numbers, and then click the Outline Numbered tab.
- If you have an existing bulleted or numbered list that you want to convert to an outline numbered list, please select the list before performing step 1, but ignore steps 3 and 4 below.
- Click a list format that does not contain the text "Heading", and then click OK.
- Type the list text, and then press ENTER after each item.
- After typing the last list text, press ENTER twice to end the list.
- To move an outline numbered item to the appropriate numbering level, do one of the following:
- To demote the item to a lower numbering level, click a list number (or anywhere in the paragraph), and click Increase Indent on the Formatting toolbar, or press ALT + SHIFT + RIGHT ARROW key.
- To bring or promote the item to a higher numbering level, click a list number (or anywhere in the paragraph, and click Decrease Indent on the Formatting toolbar, or press ALT + SHIFT + LEFT ARROW key.
Customize Bulleted or Numbered List Formats
As a sophisticated word processor, Word makes it pretty possible and easy for you to customize the appearance and other attributes of the bullets and numbering list styles. Customizing a bullet or bullet style, you basically modify the bullet or the text position (indent and alignment), or change the symbol to a picture or a symbol character that matches and can appropriately emphasize the text, or items in a list. You can also customize Numbering by modifying the number format, font in which numbering is displayed, number style (whether Roman numbers, Arabic numerals, Letters, etc), start number, or number or text position and alignment. We are going to deal with each of these in this tutorial.
Customizing a Bullet Character (Symbol) and/or Modifying Preset Settings
- If you want the customized bullet to be applied right away to an existing list, then select the list that has the bullet format you want to change, else, proceed to step 2 below.
- On the Format menu, click Bullets and Numbering, and then click the Bulleted tab in the dialog box that appears.
- Click the list format you want to modify, or the style that is closest to the format you want.
- Click Customize. The Customize Bulleted List dialog box is displayed.
- Do one or more of the following:
- To change the font formatting for the selected bullet
- Click Font and then click the Font tab in the Font dialog box appears.
- Do one or more of the following:
- To use a variant of the selected bullet instead, choose another font in the Font box. The Preview area will let you see how the bullet will appear in the selected font.
- To apply a style format to the selected bullet, click Italic, Bold, or Bold Italic in the Style box.
- To change the bullet size, select a desired size in the Size list box.
- To format bullets with a different font color than the text in the list, click the color you want in the Font color box.
- To underline the bullets, click an underline style in the Underline Style drop-down list.
- To format bullets underline with a different font color than the bullets or the text in the list, click the color you want in the Underline color box.
- Select desired options under Effects.
- Click OK (to accept the settings and then return to the Customize Bulleted List dialog box).
- To use a different symbol for bullets
- Click the Character button. The Symbol dialog box will be displayed.
- Click the symbol you want. If the symbol you want is not displayed in the grid, choose a different font from the Font box to show other character sets or variants from which you can select.
- Click OK (to accept the symbol and then return to the Customize Bulleted List dialog box).
- To use a different picture for bullets
- Click Picture to select a picture. The Picture Bullet dialog box will be displayed.
- Click the picture you want, or if you have a picture you'd like to use as bullet, click Import, select and then click Add to add it to the picture list in the Picture Bullet dialog box.
- Click OK (to accept the picture and then return to the Customize Bulleted List dialog box).
- Select any other options you want under Bullet position or Text position. In the Preview area, you'll see how your settings will look like in the document
- Click OK.
 |
| Fig: Font dialog box |
Customizing Numbered list Format
- Select the list that has the number format you want to change.
- On the Format menu, click Bullets and Numbering, and then click the Numbered or Outline Numbered tab.
- Click the list format that you want to modify, or the style that is closest to the format you want to modify.
- Click Customize. The Customize Numbered List dialog box is displayed.
- Do one or more of the following:
- To edit the numbering character, in the box under Number format, add parentheses to change "i." to "(i)", or to "i)", etc or simply change the punctuation that is used after a number or letter.
- To change the font formatting for the selected bullet
- Click Font and then click the Font tab in the Font dialog box appears.
- Do one or more of the following:
- To change the font in which the numbering character for the selected numbering style is displayed, choose another font in the Font box.
- To apply a style format to the selected numbering character, click Italic, Bold, or Bold Italic in the Style box.
- To change the numbers size, select a desired size in the Size list box.
- To format numbers with a different font color than the text in the list, click the color you want in the Font color box.
- To underline the numbers, click an underline style in the Underline Style drop-down list.
- To format numbers underline with a different font color than the numbers or the text in the list, click the color you want in the Underline color box.
- Click desired options under Effects
- Click OK (to accept the settings and then return to the Customize Numbered List dialog box).
- To change the numbers style, click a style (e.g. 1, 2, 3,...; or i, ii, iii,...; or A, B, C,...; etc) in the Number style box.
- If necessary, enter a new starting number for the list in the Start at box.
- Choose alignment and position settings you want for the selected number under Number position. See effect in the Preview area.
- Choose alignment and position settings you want for text under Text position. See effect in the Preview area.
- Click OK.
 |
| Fig: Customize Numbered list dialog box |
Customizing an Outline Numbered List Scheme
If the bullets or numbers in the outline numbered list style you selected do not appeal to you, you can easily modify the list scheme by choosing new bullets or number styles for each numbering level. You can also define further settings, such as alignment, position or indentation for bullets and text.
To modify/customize and outline numbered style- If you want the customized outline numbered list style to be applied right away to an existing outline numbered list, then select the list first, else, proceed to step 2 below.
- On the Format menu, click Bullets and Numbers, and then click the Outline Numbered List tab.
- Click a list format that does not contain the text "Heading".
- Click Customize. The Customize Outline Numbered List dialog box is displayed.
- In the Level list, click a level number that contains the bullet or number you want to modify.
- Do one of the following:
- To change the outline numbering style for the selected level to number type, click the number style/type you want in the Number Style box, and if necessary, select other relevant options for the selected level.
- To change the outline numbering style for the selected level to bullet, click the bullet type you want in the Number Style box, and if necessary, select other relevant options.
- To change the outline numbering style for the selected level to a bullet style not available in the list, click New Bullet in the Number Style box, find and click a desired symbol for the bullet in the Symbol dialog box, and then click OK.
- To change the outline numbering style for the selected level to a picture bullet not available in the list, click New Picture in the Number Style box, select the picture you want in the Picture Bullet dialog box, click OK, and if necessary, select other relevant options.
- Repeat steps 5 and 6 for each level you want to modify.
- Click OK.
 |
| Fig: Customize Outline Numbered dialog box |
Restore a Customized List Format to Its Original Setting
If you are not an expert user user of Word yet, you can easily mess things up if you make custom changes to one or more of the list formats that appear on the Bulleted, Numbered, or Outline Numbered tab. As a result, the way list items are bulleted or numbered may not be exactly professional or appealing. When that happens, Word makes it pretty easy to revert/restore the customized list format to its original setting. See the steps below.
- On the Format menu, click Bullets and Numbering. The Bullets and Numbering dialog box appears.
- Click the Bulleted, Numbered, or Outline Numbered tab.
- Click the custom list format you want to remove.
- Click Reset.
- Click OK when you are through.
 |
| Fig: Bullets and Numbering dialog box showing the Reset button |
Numbering Headings
Just like you add bullets or numbering to paragraphs to form a list, you can also format a document heading texts with numbering. Numbered headings are most commonly seen in published volumes and are very essential in creating Table of Contents, Cross-references, etc. Word has nine different built-in styles: Heading 1 through Heading 9, that you can use to format headings in a document. Using built-in Word heading styles to format headings in a document, will enable you to automatically number headings with the numbering format you choose. However, you can still create custom styles for headings in a document. In other to add numbers to the headings in the custom styles for headings you created, you'll need to link each heading to a numbered format.
See illustrative image below
 |
| Fig: Example of Numbering Headings |
To create numbered headings with built-in heading styles
- On the Format menu, click Bullets and Numbering, and then click the Outline Numbered tab.
- Click a numbering format that contains the text "Heading 1", "Heading 2", and so on, and then click OK.
- Type the text you want for the numbered heading, and then press ENTER.
- To add the next numbered heading, click the arrow next to the Style box and select the style you want.
- To move a heading to the appropriate numbering level, do one of the following:
- To demote the heading to a lower numbering level, select the heading, and click Increase Indent on the Formatting toolbar, or press the TAB key.
- To promote the heading to a higher numbering level, select the heading, and click Decrease Indent on the Formatting toolbar, or press SHIFT+TAB.
- Click OK when you are through.
Add numbers to headings with custom heading styles
Below are the steps you should use to add numbers to headings in a document formatted with custom-created heading styles in Word.
- On the Format menu, click Bullets and Numbering, and then click the Outline Numbered tab.
- Click a numbering format.
- Click Customize. The Customize Outline Numbered List dialog box is displayed.
- In the Level or the Preview box, click the heading level you want to number.
- If the dialog box is not fully expanded, click More.
- In the Link level to style box, click the style that corresponds to the level you selected in step 4.
- Repeat steps 4 through 6 for each heading style in the document.
- To move a heading to the appropriate numbering level, do one of the following:
- To demote the heading to a lower numbering level, select the heading, and click Increase Indent on the Formatting toolbar, or press the TAB key.
- To promote the heading to a higher numbering level, select the heading, and click Decrease Indent on the Formatting toolbar, or press SHIFT+TAB.
- Click OK when you are through.
Thank you for taking your time to read this tutorial. Please visit again for future updates and helpful tips. Your visits will surely be worth it. I sincerely appreciate your visits and presence here. If you are finding these tutorials and tips informative and helpful, please kindly recommend this blog to your friends. If, on the other hand, there is any area you feel improvement is needed, please kindly forward a piece of advice. These will be highly welcomed and appreciated. Feel free to drop comments or ask questions using the comment box below. Your comments will be promptly reviewed and published and your questions speedily looked into and answered in the best possible manner. Thanks.